Green Finance and Sustainable Mineral Resource Management*
12/15 2024
Author: Farhad Taghizadeh-Hesary
* This policy brief is based on the study published as Du J., Liu Y., Xu S., and Taghizadeh-Hesary F. (2024). How does green finance affect the sustainability of mineral resources? Evidence from developing countries, Journal of Cleaner Production, 475, 143620, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2024.143620
Mineral resources play a vital role in the economic development of developing nations, making the sustainability of mineral resources (SMR) a critical priority. The increasing demand for minerals such as lithium, cobalt, and rare earth elements—driven by the global energy transition—has intensified the pressure on ensuring their sustainable supply. In many developing countries, mineral extraction is often associated with inefficient resource utilization, environmental degradation, and social challenges. Integrating mineral resource management with global sustainability objectives, such as reducing carbon emissions and achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), is imperative.
Green finance offers a promising pathway by directing investments toward cleaner production methods, recycling technologies, and sustainable infrastructure, thereby promoting more responsible practices in the mineral industry.
In their 2024 study, Du et al. explored the following research questions, and this summary highlights their key findings:
• How does green finance contribute to the sustainable utilization of mineral resources in developing countries?
• Are there regional differences in the impact of green finance on mineral resource sustainability?
• What role do technological advancements and infrastructure improvements play in linking green finance to sustainable mineral resources?
• What policy measures can enhance the effectiveness of green finance in fostering sustainable mineral resource management?
Their findings provide valuable insights into how green finance can transform the mineral sector, aligning it with global sustainability goals and addressing critical regional and technological dimensions.
2.Empirical Results
The empirical results of Du et al. (2024) reveal that green finance significantly enhances the SMR with a 1% increase in green finance, resulting in a 0.363% improvement in SMR. This impact is achieved through both direct and indirect mechanisms. Green finance supports sustainable practices directly and indirectly by driving investments in technological progress and infrastructure development. Technological innovations improve resource efficiency and minimize environmental harm, while sustainable infrastructure optimizes resource utilization and reduces waste. Regional differences are also evident, with the Asia-Pacific region benefiting most from green finance, followed by Latin America and Africa, reflecting economic development and institutional capacity variations.
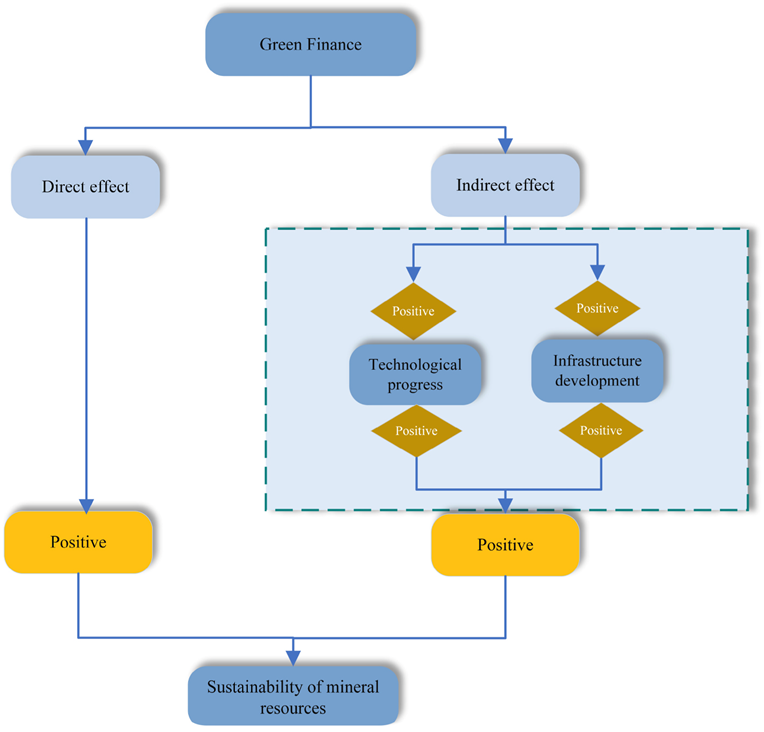
Figure 1 illustrates the pathways through which green finance influences SMR. It highlights two primary mechanisms: direct and indirect effects mediated by technological progress and infrastructure development. Both mediators have positive impacts, reinforcing green finance's dual role in fostering sustainable practices and driving innovation to support the long-term sustainability of mineral resources. This visualization complements the empirical findings by providing a clear conceptual framework for understanding the multifaceted impacts of green finance.
3.Policy Recommendations
3-1. Strengthening Green Finance Policies
Green finance policies must be refined to effectively support the sustainability of mineral resources (SMR). Tailored strategies should include enhanced tax incentives and policy support for organizations engaged in green finance activities. Financial institutions should be encouraged to innovate by developing new green products and services. Establishing a robust regulatory framework is essential to ensure the efficient allocation and proper utilization of green finance funds. Additionally, governments should consider creating dedicated green finance special funds to attract private investment and provide financial support for sustainability-focused projects in the mineral resource sector.
3-2. Increasing Fiscal Investment in Technology and Infrastructure
More significant fiscal investment is critical to advancing technological progress and improving infrastructure in the SMR sector. Allocating special funds for technological innovation and infrastructure upgrades can catalyze transformative changes. Enterprises should be incentivized to invest in research and development, with rewards for significant technological breakthroughs. Moreover, policies should foster collaboration between enterprises and research institutions to accelerate the practical application of innovative technologies within the sector.
3-3. Prioritizing Intelligent and Sustainable Infrastructure Development
The development of intelligent and environmentally sustainable infrastructure is crucial. Implementing advanced systems like smart transportation networks can optimize traffic flow and reduce energy consumption. The adoption of eco-friendly building materials can further minimize environmental impacts. A rigorous monitoring mechanism should be established to ensure these initiatives' success. This will oversee the allocation and use of funds, ensure effective implementation, and prevent inefficiencies such as waste or embezzlement. By addressing these areas, policymakers and stakeholders can create a comprehensive framework that advances sustainable practices in the mineral resource sector, fostering long-term economic and environmental benefits.
Reference:
Du J., Liu Y., Xu S., and Taghizadeh-Hesary F. (2024). How does green finance affect the sustainability of mineral resources? Evidence from developing countries, Journal of Cleaner Production, 475, 143620, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2024.143620
